By 2027, 40% of generative AI (GenAI) solutions are expected to be multimodal—encompassing text, images, audio, and video—up from just 1% in 2023, according to Gartner, Inc. This transition from single-modal to multimodal models will enhance human-AI interactions and offer opportunities for differentiating GenAI-enabled products.
Erick Brethenoux, Distinguished VP Analyst at Gartner, noted that as GenAI models increasingly incorporate multiple modalities, they can better understand relationships between diverse data types, potentially extending GenAI’s benefits across various applications and tasks. This evolution supports more comprehensive AI-human collaboration.
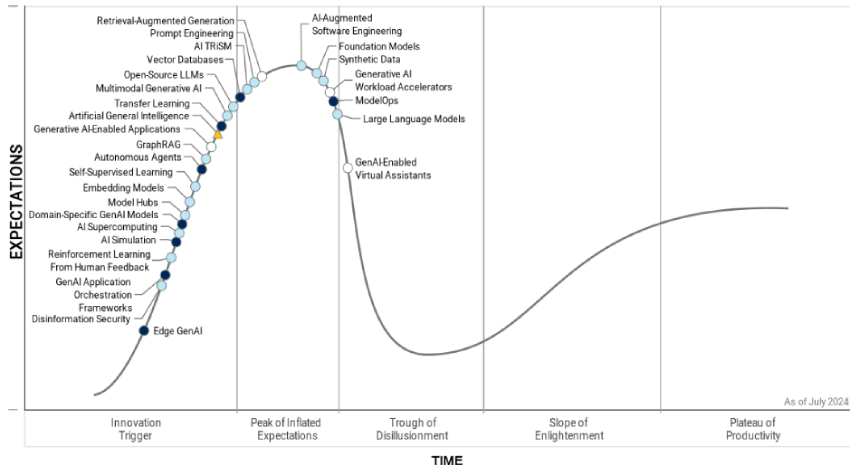
Multimodal GenAI is one of the two key technologies identified in Gartner’s 2024 Hype Cycle for Generative AI. Both multimodal GenAI and open-source large language models (LLMs) are expected to have a significant impact on organizations in the next five years.
Gartner highlights two technologies anticipated to gain mainstream adoption within the next decade: domain-specific GenAI models and autonomous agents.
Arun Chandrasekaran, Distinguished VP Analyst at Gartner, mentioned that navigating the GenAI landscape will remain challenging due to its rapidly evolving technology and vendor environment. The current phase of disillusionment will eventually give way to substantial benefits as capabilities advance swiftly over the coming years.
Multimodal GenAI
Multimodal GenAI is projected to transform enterprise applications by enabling new features and functionalities not possible with single-modal models. This technology is applicable across all industries and interaction points between AI and humans. While many current multimodal models integrate only two or three modalities, this will expand in the near future.
Brethenoux explained that since humans process information through multiple modalities like audio and visual, multimodal GenAI will provide more accurate and effective results by reducing latency and improving overall quality compared to single-modality models.
Open-Source LLMs
Open-source LLMs are foundational models that enhance enterprise value by providing democratized access and allowing for customization specific to tasks and use cases. They foster innovation through community collaboration, improve privacy and security, and reduce dependency on single vendors. Chandrasekaran highlighted that these models are easier and more cost-effective to train, benefiting business applications and processes.
Domain-Specific GenAI Models
Domain-specific GenAI models are tailored for particular industries or tasks, offering improved accuracy, security, and contextual relevance. They can accelerate value delivery and reduce the need for complex prompt engineering compared to general-purpose models, thus mitigating risks of inaccurate outputs and promoting broader GenAI adoption.
Chandrasekaran emphasized that these specialized models provide a more robust foundation for industry-specific applications, leading to faster and more secure AI project outcomes.
Autonomous Agents
Autonomous agents are systems capable of achieving set goals without human input, using AI techniques to make decisions, execute actions, and adapt based on their environment. These agents can handle complex tasks, improve over time, and enhance business operations and customer experiences, offering potential cost savings and a competitive edge.
Brethenoux remarked that autonomous agents represent a significant advancement in AI, enabling independent decision-making and operation that can lead to more efficient business processes and new opportunities, though they may also shift workforce roles from execution to oversight.
 Latest Technology News Today – Get Latest Information Technology Updates and Services Latest Technology News Today – Get Latest Information Technology Updates and Services
Latest Technology News Today – Get Latest Information Technology Updates and Services Latest Technology News Today – Get Latest Information Technology Updates and Services 









